Explain Non-Maximum Suppression and build it from scratch
Published:
Xin chào các bạn! Trong bài viết này, mình sẽ hướng dẫn chi tiết về giải thuật Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) - một kỹ thuật quan trọng trong khâu post-processing của các mô hình YOLO. Đây là kiến thức bắt buộc khi bạn muốn deploy YOLO model lên production.
📑 Mục Lục
- NMS Giải Quyết Vấn Đề Gì?
- Intersection over Union (IoU)
- Thuật Toán NMS Hoạt Động Như Thế Nào?
- Implement NMS Từ Đầu
- Tips & Best Practices
- FAQs - Câu Hỏi Thường Gặp
1. NMS Giải Quyết Vấn Đề Gì?
1.1. Vấn Đề Khi Deploy YOLO Models
Nếu bạn đã từng sử dụng thư viện Ultralytics để chạy YOLOv8, YOLOv5, output mà bạn nhận được thường ở định dạng đã được xử lý sẵn:
x_center, y_center, width, height, class, confidence_score
Tuy nhiên, đây là output đã được hậu xử lý. Khi bạn convert model sang các format khác như:
- ONNX (cho cross-platform deployment)
- TFLite (cho mobile devices)
- TensorRT (cho NVIDIA GPUs)
- OpenVINO (cho Intel hardware)
- CoreML (cho iOS devices)
Thì output thô của model sẽ có dạng:
Shape: (1, 84, 8400) hoặc (1, 8400, 84)
Trong đó:
- 8400: Số lượng detection boxes (anchor points từ các feature maps)
- 80×80 = 6,400 (stride 8)
- 40×40 = 1,600 (stride 16)
- 20×20 = 400 (stride 32)
- Tổng: 8,400 predictions
- 84:
4 tọa độ + 80 classes(với COCO dataset)
1.2. Tại Sao Cần Phải Hiểu NMS?
Khi deploy trên các nền tảng khác nhau:
| Platform | Ngôn Ngữ | Cần Implement NMS |
|---|---|---|
| Web | JavaScript | ✅ Có |
| Mobile (Android) | Java/Kotlin | ✅ Có |
| Mobile (iOS) | Swift | ✅ Có |
| Embedded | C++ | ✅ Có |
| Edge Devices | C/C++ | ✅ Có |
Khâu hậu xử lý (post-processing) của tác giả viết bằng Python sẽ KHÔNG được đính kèm sau khi convert. Điều này buộc bạn phải tự implement lại NMS.
1.3. NMS Làm Gì?
 Hình 1: Trước NMS (trái) vs Sau NMS (phải)
Hình 1: Trước NMS (trái) vs Sau NMS (phải)
NMS loại bỏ các bounding boxes trùng lặp và chỉ giữ lại những boxes tốt nhất cho mỗi object.
Ví dụ: Khi detect một con chó, model có thể tạo ra 50-100 boxes cho cùng 1 object. NMS sẽ chọn box tốt nhất và loại bỏ các boxes còn lại.
2. Intersection over Union (IoU)
IoU là nền tảng của thuật toán NMS. Đây là metric đo độ trùng lặp giữa 2 bounding boxes.
2.1. Công Thức IoU
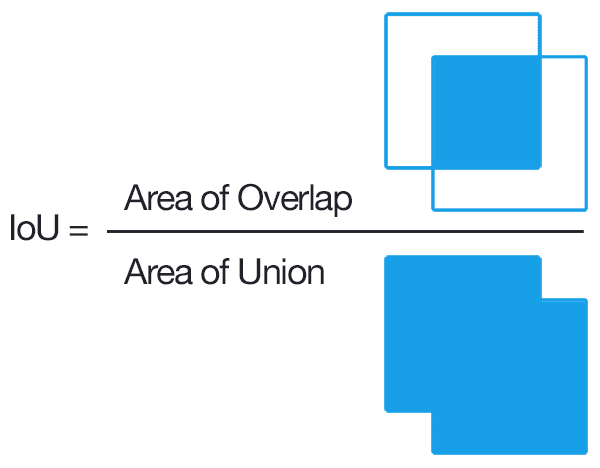 Hình 2: Công thức tính IoU
Hình 2: Công thức tính IoU
IoU = Area of Intersection / Area of Union
2.2. Ví Dụ Tính IoU
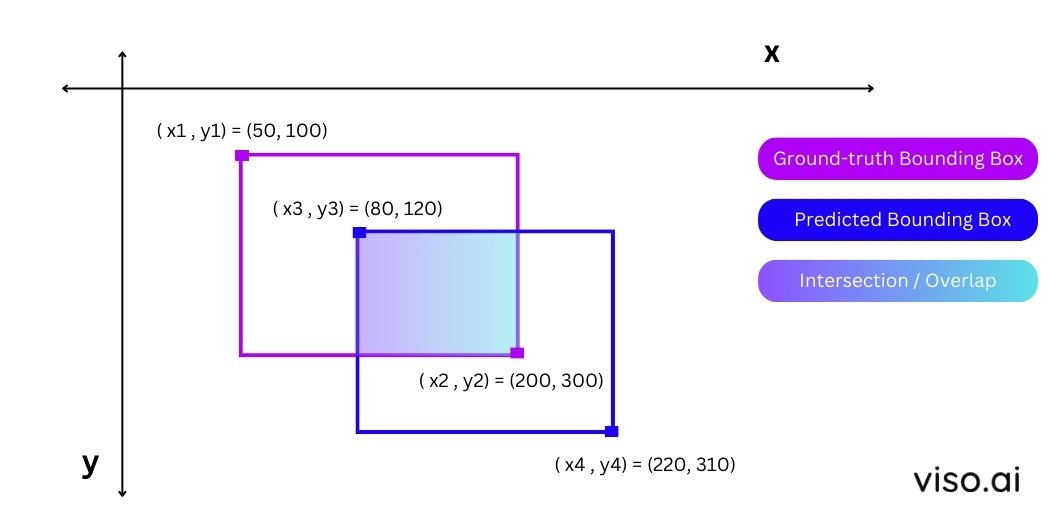 Hình 3: Ví dụ minh họa tính IoU
Hình 3: Ví dụ minh họa tính IoU
Cho 2 boxes:
- Box 1: Góc trái trên (50, 100), góc phải dưới (200, 300)
- Box 2: Góc trái trên (80, 120), góc phải dưới (220, 310)
Bước 1: Tính tọa độ phần giao (Intersection)
x_left = max(50, 80) = 80
y_top = max(100, 120) = 120
x_right = min(200, 220) = 200
y_bottom = min(300, 310) = 300
Bước 2: Tính diện tích giao
intersection_width = 200 - 80 = 120
intersection_height = 300 - 120 = 180
intersection_area = 120 × 180 = 21,600
Bước 3: Tính diện tích hợp
box1_area = (200 - 50) × (300 - 100) = 150 × 200 = 30,000
box2_area = (220 - 80) × (310 - 120) = 140 × 190 = 26,600
union_area = box1_area + box2_area - intersection_area
union_area = 30,000 + 26,600 - 21,600 = 35,000
Bước 4: Tính IoU
IoU = 21,600 / 35,000 = 0.617 (≈ 61.7%)
2.3. Code Implementation IoU
def calculate_iou(box1, box2):
"""
Tính IoU giữa 2 bounding boxes
Args:
box1: [x1, y1, x2, y2] - tọa độ góc trái trên và phải dưới
box2: [x1, y1, x2, y2]
Returns:
iou: float - giá trị IoU từ 0 đến 1
"""
# Tìm tọa độ vùng giao
x_left = max(box1[0], box2[0])
y_top = max(box1[1], box2[1])
x_right = min(box1[2], box2[2])
y_bottom = min(box1[3], box2[3])
# Kiểm tra có giao không
if x_right < x_left or y_bottom < y_top:
return 0.0
# Tính diện tích giao
intersection_area = (x_right - x_left) * (y_bottom - y_top)
# Tính diện tích mỗi box
box1_area = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1])
box2_area = (box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1])
# Tính diện tích hợp
union_area = box1_area + box2_area - intersection_area
# Tính IoU
iou = intersection_area / union_area if union_area > 0 else 0
return iou
# Test function
box1 = [50, 100, 200, 300]
box2 = [80, 120, 220, 310]
print(f"IoU = {calculate_iou(box1, box2):.4f}") # Output: IoU = 0.6171
2.4. Ý Nghĩa Của IoU Threshold
| IoU Value | Ý Nghĩa | Quyết Định NMS |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 - 0.3 | Không trùng hoặc trùng ít | ✅ Giữ cả 2 boxes |
| 0.3 - 0.5 | Trùng vừa phải | ⚠️ Tùy threshold |
| 0.5 - 0.7 | Trùng nhiều | ❌ Loại box có conf thấp |
| 0.7 - 1.0 | Trùng rất nhiều | ❌ Chắc chắn loại |
Recommended IoU thresholds:
- 0.45 - 0.5: Cho objects nhỏ, chen chúc (crowded scenes)
- 0.5 - 0.6: Cân bằng tốt cho hầu hết trường hợp
- 0.6 - 0.7: Cho objects lớn, rời rạc
3. Thuật Toán NMS Hoạt Động Như Thế Nào?
3.1. Overview - Quy Trình 5 Bước
Input: 8400 predictions (mỗi prediction có 84 giá trị)
↓
[Step 1] Filter by Confidence Threshold
↓ (giữ lại ~100-500 boxes)
[Step 2] Extract Class & Confidence
↓
[Step 3] Group by Class
↓
[Step 4] Apply NMS per Class
↓
[Step 5] Combine Results
↓
Output: Final detections (x, y, w, h, class, conf)
3.2. Chi Tiết Từng Bước
Step 1: Lọc Theo Confidence Threshold
Input format: Mỗi detection có dạng vector 84 giá trị:
[x_center, y_center, width, height, score_class0, score_class1, ..., score_class79]
↑________bbox coords_______↑ ↑____________80 class scores_________________↑
Ví dụ minh họa:
Giả sử detection vector:
detection = [0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.15, # bbox: x, y, w, h
0.02, 0.91, 0.05, ..., 0.01] # 80 class scores
Với conf_threshold = 0.5:
max_score = max(detection[4:]) = 0.91 # score của class 1 (person)
if max_score > 0.5:
keep_this_detection = True # ✅ GIỮ LẠI
else:
discard_detection = True # ❌ LOẠI BỎ
Tại sao các scores không tổng = 1?
YOLO sử dụng Sigmoid activation cho mỗi class (không phải Softmax):
- Cho phép multi-label detection (1 object có thể thuộc nhiều class)
- Mỗi class score độc lập:
sigmoid(x) ∈ [0, 1]
Ví dụ: Một object có thể vừa là “person” (0.9) vừa là “tennis racket” (0.8)
Step 2: Extract Class ID & Max Confidence
# Trước Step 2
detection = [0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.15, 0.02, 0.91, 0.05, ..., 0.01]
# Sau Step 2
class_id = argmax([0.02, 0.91, 0.05, ..., 0.01]) = 1 # class "person"
max_conf = max([0.02, 0.91, 0.05, ..., 0.01]) = 0.91
# Output format mới
processed_detection = [0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.15, 1, 0.91]
# ↑___bbox coords___↑ ↑cls↑conf
Note: Trong thực tế, Step 1 và Step 2 được thực hiện cùng lúc để tối ưu performance.
Step 3: Group Detections By Class
Mục đích: Tách các detections theo từng class để xử lý riêng biệt.
# Input: Tất cả detections sau Step 2
all_detections = [
[100, 200, 50, 80, 0, 0.9], # person
[150, 220, 48, 75, 0, 0.85], # person (trùng với detection trên)
[500, 300, 60, 90, 1, 0.92], # bicycle
[120, 210, 52, 78, 0, 0.88], # person (cũng trùng)
[510, 305, 58, 88, 1, 0.87], # bicycle (trùng với bicycle trên)
]
# Output: Grouped by class
class_0_detections = [ # person
[100, 200, 50, 80, 0, 0.9],
[150, 220, 48, 75, 0, 0.85],
[120, 210, 52, 78, 0, 0.88],
]
class_1_detections = [ # bicycle
[500, 300, 60, 90, 1, 0.92],
[510, 305, 58, 88, 1, 0.87],
]
Tại sao phải group by class?
- Tránh loại bỏ nhầm detections của các objects khác nhau
- Ví dụ: Person box và Car box có thể overlap nhưng là 2 objects khác nhau
Step 4: Apply NMS Per Class (Bước quan trọng nhất!)
Thuật toán NMS cho 1 class:
def nms_single_class(detections, iou_threshold=0.5):
"""
Input:
detections = [[x1,y1,x2,y2,class,conf], ...] # N detections
iou_threshold = 0.5
Output:
kept_detections = [[x1,y1,x2,y2,class,conf], ...] # M detections (M < N)
"""
# Bước 1: Sắp xếp theo confidence score giảm dần
sorted_detections = sort_by_confidence_desc(detections)
kept_boxes = []
# Bước 2: Loop qua từng detection
while len(sorted_detections) > 0:
# Lấy box có confidence cao nhất
best_box = sorted_detections[0]
kept_boxes.append(best_box)
# Bước 3: Tính IoU của best_box với tất cả boxes còn lại
remaining_boxes = []
for box in sorted_detections[1:]:
iou = calculate_iou(best_box, box)
# Nếu IoU < threshold → giữ lại (không trùng)
if iou < iou_threshold:
remaining_boxes.append(box)
# Nếu IoU >= threshold → loại bỏ (trùng lặp)
sorted_detections = remaining_boxes
return kept_boxes
Minh họa bằng ví dụ cụ thể:
# Giả sử có 4 person detections (đã sort theo conf)
person_detections = [
[100, 200, 150, 280, 0, 0.92], # Box A - BEST
[105, 205, 155, 285, 0, 0.88], # Box B - overlap với A
[110, 202, 152, 282, 0, 0.85], # Box C - overlap với A
[400, 300, 450, 400, 0, 0.80], # Box D - person khác
]
# Iteration 1:
# - Chọn Box A (conf=0.92) → KEEP
# - Tính IoU(A, B) = 0.85 > 0.5 → REMOVE B
# - Tính IoU(A, C) = 0.78 > 0.5 → REMOVE C
# - Tính IoU(A, D) = 0.02 < 0.5 → KEEP D
# Remaining: [Box D]
# Iteration 2:
# - Chọn Box D (conf=0.80) → KEEP
# Remaining: []
# Final result:
kept_boxes = [
[100, 200, 150, 280, 0, 0.92], # Box A
[400, 300, 450, 400, 0, 0.80], # Box D
]
Flowchart của NMS:
START
↓
Sort boxes by confidence (desc)
↓
Pick highest confidence box → ADD to output
↓
Calculate IoU with all remaining boxes
↓
Remove boxes with IoU > threshold
↓
Any boxes left?
├─ YES → Go back to "Pick highest"
└─ NO → END
Step 5: Combine All Classes
# Kết hợp kết quả từ tất cả các classes
final_detections = []
for class_id in range(num_classes):
class_detections = group_by_class[class_id]
kept_detections = nms_single_class(class_detections, iou_threshold=0.5)
final_detections.extend(kept_detections)
# final_detections chính là output cuối cùng!
3.3. Class-Aware vs Class-Agnostic NMS
| Class-Aware NMS | Class-Agnostic NMS | |
|---|---|---|
| Cách hoạt động | Chạy NMS riêng cho từng class | Chạy NMS trên TẤT CẢ boxes cùng lúc |
| Ưu điểm | Không loại nhầm objects khác class | Nhanh hơn, đơn giản hơn |
| Nhược điểm | Chậm hơn khi có nhiều classes | Có thể loại nhầm overlapping objects |
| Use case | YOLO standard, crowded scenes | Real-time apps, single/few classes |
Ví dụ so sánh:
# Scenario: Person đứng cạnh bicycle, 2 boxes overlap 60%
person_box = [100, 200, 150, 300, 0, 0.9] # class 0: person
bicycle_box = [120, 210, 180, 310, 1, 0.85] # class 1: bicycle
# Class-Aware NMS:
# → Xử lý riêng person và bicycle
# → GIỮ CẢ 2 BOXES ✅
# Class-Agnostic NMS:
# → Xử lý chung tất cả
# → IoU = 0.6 > threshold
# → Chỉ giữ person_box (conf cao hơn) ❌ SAI!
Kết luận: Class-Aware NMS tốt hơn cho general object detection.
4. Implement NMS Từ Đầu
4.1. Setup Environment
# Import thư viện cần thiết
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
import onnxruntime as ort
# Load ONNX model
model = ort.InferenceSession(
"./yolov8n.onnx",
providers=["CPUExecutionProvider"]
)
# Kiểm tra input/output shape
inputs = model.get_inputs()
outputs = model.get_outputs()
print("=" * 50)
print("MODEL INFORMATION")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"Input Name: {inputs[0].name}")
print(f"Input Type: {inputs[0].type}")
print(f"Input Shape: {inputs[0].shape}")
print("-" * 50)
print(f"Output Name: {outputs[0].name}")
print(f"Output Type: {outputs[0].type}")
print(f"Output Shape: {outputs[0].shape}")
print("=" * 50)
Expected Output:
==================================================
MODEL INFORMATION
==================================================
Input Name: images
Input Type: tensor(float)
Input Shape: [1, 3, 640, 640]
--------------------------------------------------
Output Name: output0
Output Type: tensor(float)
Output Shape: [1, 84, 8400]
==================================================
4.2. Image Preprocessing
def preprocess_image(image_path, target_size=640):
"""
Tiền xử lý ảnh cho YOLO model
Args:
image_path: Đường dẫn đến ảnh
target_size: Kích thước input của model (mặc định 640)
Returns:
original_image: Ảnh gốc (BGR format)
preprocessed_image: Ảnh đã xử lý (shape: 1, 3, 640, 640)
"""
# Đọc ảnh
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
original_image = image.copy()
print(f"📷 Original image shape: {image.shape}")
# Convert BGR → RGB
rgb_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Resize về 640x640
resized_image = cv2.resize(rgb_image, (target_size, target_size))
# Normalize [0, 255] → [0, 1]
normalized_image = resized_image.astype("float32") / 255.0
# Transpose (H, W, C) → (C, H, W)
transposed_image = normalized_image.transpose(2, 0, 1)
# Add batch dimension (C, H, W) → (1, C, H, W)
preprocessed_image = transposed_image[np.newaxis, ...]
print(f"🔧 Preprocessed shape: {preprocessed_image.shape}")
return original_image, preprocessed_image
# Test preprocessing
original_img, preprocessed_img = preprocess_image("./demo.jpg")
4.3. Run Inference
# Chạy model inference
predictions = model.run(
["output0"], # output names
{"images": preprocessed_img} # input dict
)[0]
print(f"🎯 Raw prediction shape: {predictions.shape}")
# Output: (1, 84, 8400)
# Transpose để dễ xử lý
predictions = predictions.transpose(0, 2, 1)[0]
print(f"🔄 Transposed shape: {predictions.shape}")
# Output: (8400, 84)
4.4. Implement NMS - Complete Code
Function 1: Parse & Filter Predictions (Step 1 & 2)
def parse_predictions(
predictions,
img_width,
img_height,
conf_threshold=0.5,
model_input_size=640
):
"""
Parse YOLO predictions và filter theo confidence threshold
Args:
predictions: Array shape (8400, 84) từ YOLO model
img_width: Chiều rộng ảnh gốc
img_height: Chiều cao ảnh gốc
conf_threshold: Ngưỡng confidence tối thiểu (default: 0.5)
model_input_size: Kích thước input model (default: 640)
Returns:
filtered_boxes: Array shape (N, 6) với format:
[x1, y1, x2, y2, class_id, confidence]
"""
# Step 1: Tính max confidence score cho mỗi detection
# predictions[:, 4:] lấy 80 class scores
max_conf_scores = np.max(predictions[:, 4:], axis=1)
# Step 2: Lọc detections có conf > threshold
valid_indices = np.where(max_conf_scores > conf_threshold)[0]
if len(valid_indices) == 0:
print("⚠️ No detections above confidence threshold!")
return np.array([])
# Lấy các detections hợp lệ
valid_detections = predictions[valid_indices]
print(f"✅ Filtered: {len(valid_detections)}/{len(predictions)} detections")
# Step 3: Extract class_id và confidence
class_ids = valid_detections[:, 4:].argmax(axis=1)
confidences = valid_detections[:, 4:].max(axis=1)
# Step 4: Convert từ center format → corner format
# YOLO output: [x_center, y_center, width, height] (normalized 0-1)
# Cần convert sang: [x1, y1, x2, y2] (pixel coordinates)
x_centers = valid_detections[:, 0]
y_centers = valid_detections[:, 1]
widths = valid_detections[:, 2]
heights = valid_detections[:, 3]
# Rescale về tọa độ ảnh gốc
scale_x = img_width / model_input_size
scale_y = img_height / model_input_size
x1 = ((x_centers - widths / 2) / model_input_size) * img_width
y1 = ((y_centers - heights / 2) / model_input_size) * img_height
x2 = ((x_centers + widths / 2) / model_input_size) * img_width
y2 = ((y_centers + heights / 2) / model_input_size) * img_height
# Clip coordinates về giới hạn ảnh
x1 = np.clip(x1, 0, img_width)
y1 = np.clip(y1, 0, img_height)
x2 = np.clip(x2, 0, img_width)
y2 = np.clip(y2, 0, img_height)
# Combine tất cả thông tin
filtered_boxes = np.hstack([
x1[:, np.newaxis],
y1[:, np.newaxis],
x2[:, np.newaxis],
y2[:, np.newaxis],
class_ids[:, np.newaxis],
confidences[:, np.newaxis]
])
return filtered_boxes
Function 2: NMS for Single Class (Step 4)
def nms_single_class(boxes, scores, iou_threshold=0.5):
"""
Apply Non-Maximum Suppression cho 1 class
Args:
boxes: Array shape (N, 4) với format [x1, y1, x2, y2]
scores: Array shape (N,) - confidence scores
iou_threshold: Ngưỡng IoU để loại bỏ boxes trùng lặp
Returns:
keep_indices: Array indices của các boxes được giữ lại
"""
if len(boxes) == 0:
return np.array([], dtype=np.int32)
# Extract coordinates
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
# Tính diện tích mỗi box
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
# Sort indices theo confidence score giảm dần
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
# Lấy index của box có confidence cao nhất
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
# Nếu chỉ còn 1 box → kết thúc
if order.size == 1:
break
# Tính IoU của box hiện tại với tất cả boxes còn lại
# Tìm tọa độ vùng giao
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
# Tính width và height của vùng giao
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
# Tính diện tích giao
intersection = w * h
# Tính IoU
iou = intersection / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - intersection)
# Giữ lại các boxes có IoU <= threshold (không trùng)
inds = np.where(iou <= iou_threshold)[0]
# Update order (cộng 1 vì đã bỏ qua phần tử đầu)
order = order[inds + 1]
return np.array(keep, dtype=np.int32)
Function 3: Apply NMS All Classes (Step 3, 4, 5)
def apply_nms(filtered_boxes, iou_threshold=0.5):
"""
Apply Class-Aware NMS trên tất cả detections
Args:
filtered_boxes: Array shape (N, 6)
[x1, y1, x2, y2, class_id, confidence]
iou_threshold: Ngưỡng IoU (default: 0.5)
Returns:
final_boxes: Array các boxes sau NMS
"""
if len(filtered_boxes) == 0:
return np.array([])
# Step 3: Lấy danh sách unique classes
unique_classes = np.unique(filtered_boxes[:, 4])
print(f"\n🎨 Detected classes: {unique_classes.astype(int)}")
final_indices = []
# Step 4: Loop qua từng class và apply NMS
for class_id in unique_classes:
# Lấy indices của class này
class_indices = np.where(filtered_boxes[:, 4] == class_id)[0]
class_boxes = filtered_boxes[class_indices, :4] # x1,y1,x2,y2
class_scores = filtered_boxes[class_indices, 5] # confidence
print(f" Class {int(class_id)}: {len(class_boxes)} boxes before NMS")
# Apply NMS cho class này
keep_indices = nms_single_class(
class_boxes,
class_scores,
iou_threshold
)
# Chuyển về indices global
global_keep_indices = class_indices[keep_indices]
final_indices.extend(global_keep_indices)
print(f" Class {int(class_id)}: {len(keep_indices)} boxes after NMS ✓")
# Step 5: Combine results
final_boxes = filtered_boxes[final_indices]
print(f"\n📦 Final detections: {len(final_boxes)}")
return final_boxes
4.5. Complete Pipeline
# COCO class names (80 classes)
COCO_CLASSES = [
"person", "bicycle", "car", "motorcycle", "airplane", "bus", "train",
"truck", "boat", "traffic light", "fire hydrant", "stop sign",
"parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog", "horse", "sheep", "cow",
"elephant", "bear", "zebra", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella",
"handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee", "skis", "snowboard",
"sports ball", "kite", "baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard",
"surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork",
"knife", "spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange",
"broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza", "donut", "cake", "chair",
"couch", "potted plant", "bed", "dining table", "toilet", "tv",
"laptop", "mouse", "remote", "keyboard", "cell phone", "microwave",
"oven", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator", "book", "clock", "vase",
"scissors", "teddy bear", "hair drier", "toothbrush"
]
def yolo_postprocess_complete(
image_path,
model,
conf_threshold=0.5,
iou_threshold=0.5
):
"""
Complete YOLO post-processing pipeline
Args:
image_path: Đường dẫn ảnh
model: ONNX model session
conf_threshold: Confidence threshold
iou_threshold: IoU threshold for NMS
Returns:
final_detections: Array các detections cuối cùng
original_image: Ảnh gốc để visualize
"""
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("YOLO POST-PROCESSING PIPELINE")
print("="*60)
# 1. Preprocess
print("\n[1/5] Preprocessing image...")
original_image, preprocessed_image = preprocess_image(image_path)
img_height, img_width = original_image.shape[:2]
# 2. Inference
print("\n[2/5] Running model inference...")
predictions = model.run(
["output0"],
{"images": preprocessed_image}
)[0]
predictions = predictions.transpose(0, 2, 1)[0] # (8400, 84)
# 3. Parse & Filter
print(f"\n[3/5] Parsing predictions (conf > {conf_threshold})...")
filtered_boxes = parse_predictions(
predictions,
img_width,
img_height,
conf_threshold=conf_threshold
)
if len(filtered_boxes) == 0:
print("\n❌ No detections found!")
return np.array([]), original_image
# 4. Apply NMS
print(f"\n[4/5] Applying NMS (IoU threshold: {iou_threshold})...")
final_detections = apply_nms(filtered_boxes, iou_threshold=iou_threshold)
# 5. Print results
print("\n[5/5] Final Results:")
print("="*60)
for det in final_detections:
x1, y1, x2, y2, class_id, conf = det
class_name = COCO_CLASSES[int(class_id)]
print(f" 📍 {class_name:15s} | Conf: {conf:.3f} | "
f"Box: [{int(x1)}, {int(y1)}, {int(x2)}, {int(y2)}]")
print("="*60)
return final_detections, original_image
# Run complete pipeline
final_dets, orig_img = yolo_postprocess_complete(
image_path="./demo.jpg",
model=model,
conf_threshold=0.5,
iou_threshold=0.5
)
4.6. Visualization
def visualize_detections(image, detections, class_names=COCO_CLASSES):
"""
Vẽ bounding boxes và labels lên ảnh
Args:
image: Ảnh gốc (BGR format)
detections: Array shape (N, 6)
class_names: List tên các classes
"""
# Copy ảnh để không modify original
vis_image = image.copy()
# Generate colors cho mỗi class
np.random.seed(42)
colors = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(len(class_names), 3))
for det in detections:
x1, y1, x2, y2, class_id, conf = det
class_id = int(class_id)
# Get color và class name
color = colors[class_id].tolist()
class_name = class_names[class_id]
# Vẽ bounding box
cv2.rectangle(
vis_image,
(int(x1), int(y1)),
(int(x2), int(y2)),
color,
thickness=2
)
# Tạo label text
label = f"{class_name} {conf:.2f}"
# Tính kích thước text
(text_width, text_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(
label,
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6,
1
)
# Vẽ background cho text
cv2.rectangle(
vis_image,
(int(x1), int(y1) - text_height - 10),
(int(x1) + text_width, int(y1)),
color,
-1
)
# Vẽ text
cv2.putText(
vis_image,
label,
(int(x1), int(y1) - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6,
(255, 255, 255),
thickness=2
)
return vis_image
# Visualize kết quả
result_image = visualize_detections(orig_img, final_dets)
# Display
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(result_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('YOLO Detection Results After NMS', fontsize=16)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('detection_result.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
print("✅ Saved result to 'detection_result.png'")
4.7. Performance Benchmarking
import time
def benchmark_nms(image_path, model, num_runs=10):
"""
Đo performance của NMS pipeline
"""
print(f"\n⏱️ Running benchmark ({num_runs} iterations)...")
times = {
'preprocess': [],
'inference': [],
'postprocess': [],
'total': []
}
for i in range(num_runs):
t_total_start = time.time()
# Preprocess
t1 = time.time()
orig_img, prep_img = preprocess_image(image_path)
t2 = time.time()
times['preprocess'].append(t2 - t1)
# Inference
t1 = time.time()
pred = model.run(["output0"], {"images": prep_img})[0]
pred = pred.transpose(0, 2, 1)[0]
t2 = time.time()
times['inference'].append(t2 - t1)
# Postprocess
t1 = time.time()
filtered = parse_predictions(pred, orig_img.shape[1], orig_img.shape[0])
final = apply_nms(filtered)
t2 = time.time()
times['postprocess'].append(t2 - t1)
times['total'].append(time.time() - t_total_start)
# Print results
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("PERFORMANCE BENCHMARK RESULTS")
print("="*60)
for stage, stage_times in times.items():
avg = np.mean(stage_times) * 1000
std = np.std(stage_times) * 1000
print(f"{stage:15s}: {avg:6.2f} ± {std:5.2f} ms")
print("="*60)
total_avg = np.mean(times['total']) * 1000
fps = 1000 / total_avg
print(f"Average FPS: {fps:.1f}")
print("="*60)
# Run benchmark
benchmark_nms("./demo.jpg", model, num_runs=10)
5. Tips & Best Practices
5.1. Chọn Confidence Threshold
| Use Case | Recommended conf_threshold | Lý do |
|---|---|---|
| General purpose | 0.5 - 0.6 | Cân bằng precision/recall |
| High precision needed | 0.7 - 0.8 | Giảm false positives |
| High recall needed | 0.3 - 0.4 | Detect nhiều objects, chấp nhận FP |
| Real-time application | 0.6 - 0.7 | Giảm số boxes cần xử lý → nhanh hơn |
Cách tuning:
# Test với nhiều thresholds
thresholds = [0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7]
for thresh in thresholds:
dets, _ = yolo_postprocess_complete(
"test.jpg", model,
conf_threshold=thresh
)
print(f"Threshold {thresh}: {len(dets)} detections")
5.2. Chọn IoU Threshold
| Scenario | Recommended iou_threshold | Ví dụ |
|---|---|---|
| Crowded scenes | 0.3 - 0.4 | Crowd counting, traffic |
| Normal scenes | 0.5 - 0.6 | General detection |
| Sparse objects | 0.6 - 0.7 | Large objects, few overlaps |
Rule of thumb:
- IoU càng thấp → càng aggressive (loại nhiều boxes)
- IoU càng cao → càng conservative (giữ nhiều boxes)
5.3. Tối Ưu Performance
Vectorized Operations
# ❌ BAD: Loop từng box
def slow_nms(boxes, scores, iou_thresh):
keep = []
for i in range(len(boxes)):
if i in removed:
continue
for j in range(i+1, len(boxes)):
iou = calculate_iou(boxes[i], boxes[j])
if iou > iou_thresh:
removed.add(j)
return keep
# ✅ GOOD: Vectorized operations
def fast_nms(boxes, scores, iou_thresh):
# Tính tất cả IoUs cùng lúc
ious = calculate_iou_matrix(boxes) # vectorized
# ... rest of NMS logic
Performance gain: ~10-50x faster!
Early Stopping
# Nếu số detections quá nhiều → tăng conf_threshold
if len(filtered_boxes) > 1000:
print("⚠️ Too many detections, increase conf_threshold!")
filtered_boxes = filtered_boxes[filtered_boxes[:, 5] > 0.7]
5.4. Common Pitfalls
Pitfall 1: Quên Rescale Coordinates
# ❌ SAI: Giữ nguyên tọa độ normalized
x1 = (x_center - width/2) # sẽ ra giá trị 0-1
# ✅ ĐÚNG: Rescale về pixel coordinates
x1 = ((x_center - width/2) / 640) * img_width
Pitfall 2: Dùng Class-Agnostic NMS Khi Có Overlapping Objects
# ❌ SAI: NMS chung cho tất cả classes
all_boxes = combine_all_classes(detections)
keep = nms(all_boxes) # Có thể loại nhầm!
# ✅ ĐÚNG: NMS riêng cho từng class
for class_id in unique_classes:
class_boxes = filter_by_class(detections, class_id)
keep = nms(class_boxes)
Pitfall 3: Không Clip Coordinates
# ❌ SAI: Coordinates có thể âm hoặc vượt quá ảnh
x1, y1, x2, y2 = convert_coords(...)
# ✅ ĐÚNG: Clip về giới hạn ảnh
x1 = np.clip(x1, 0, img_width)
y1 = np.clip(y1, 0, img_height)
x2 = np.clip(x2, 0, img_width)
y2 = np.clip(y2, 0, img_height)
5.5. Debugging Tips
# Visualize intermediate results
def debug_nms(image, detections, stage_name):
"""Vẽ detections ở mỗi stage"""
vis = visualize_detections(image, detections)
cv2.imwrite(f"debug_{stage_name}.jpg", vis)
print(f"💾 Saved {stage_name}: {len(detections)} boxes")
# Usage
filtered = parse_predictions(...)
debug_nms(image, filtered, "after_filtering")
final = apply_nms(filtered)
debug_nms(image, final, "after_nms")
6. FAQ - Câu Hỏi Thường Gặp
Q1: Tại sao sau khi convert sang ONNX, số lượng detections lại nhiều hơn khi dùng Ultralytics?
A: Vì Ultralytics đã apply NMS với default settings (conf=0.25, iou=0.45). Khi bạn convert, bạn nhận raw output chưa qua NMS.
# Ultralytics internals (hidden from user)
results = model.predict("image.jpg")
# ↑ Đã apply NMS inside
# ONNX (raw output)
raw_output = onnx_model.run(...)
# ↑ Chưa apply NMS, bạn phải tự làm
Q2: Class-Aware NMS có chậm hơn Class-Agnostic NMS nhiều không?
A: Có, nhưng không đáng kể trong most cases:
# Benchmark results (10,000 detections, 80 classes)
Class-Agnostic NMS: ~15ms
Class-Aware NMS: ~25ms
# Chỉ chậm hơn ~10ms, acceptable!
Trade-off này đáng giá vì accuracy cao hơn nhiều.
Q3: Làm sao để detect objects rất nhỏ (small objects)?
Tips:
- Giảm
conf_threshold: 0.3 - 0.4 thay vì 0.5 - Giảm
iou_threshold: 0.4 thay vì 0.5 - Tăng resolution: Train/inference ở 1280 thay vì 640
- Multi-scale testing: Inference nhiều scales rồi combine
# Multi-scale inference
scales = [640, 800, 1024]
all_detections = []
for scale in scales:
dets = inference(image, scale)
all_detections.extend(dets)
final = apply_nms(all_detections)
Q4: Có thể dùng Soft-NMS thay vì Hard-NMS không?
A: Có! Soft-NMS giảm score thay vì loại bỏ hoàn toàn.
def soft_nms(boxes, scores, iou_thresh=0.5, sigma=0.5):
"""
Soft-NMS: Giảm score thay vì remove
"""
for i in range(len(boxes)):
max_idx = scores.argmax()
# Tính IoU
ious = calculate_iou(boxes[max_idx], boxes)
# Decay scores thay vì remove
decay = np.exp(-(ious ** 2) / sigma)
scores = scores * decay
scores[max_idx] = -1 # Đã xử lý
return keep_indices
Soft-NMS tốt hơn cho:
- Overlapping objects (people in crowd)
- Occlusion cases
Q5: Output của YOLO có thể khác 8400 không?
A: Có! Phụ thuộc vào kiến trúc:
| Model | Input Size | Output Shape | Số Detections |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 640 | (1, 84, 8400) | 8,400 |
| YOLOv8n | 1280 | (1, 84, 33600) | 33,600 |
| YOLOv5 | 640 | (1, 25200, 85) | 25,200 |
Công thức: num_detections = Σ(feature_map_h × feature_map_w)
Q6: Làm sao để deploy NMS lên JavaScript/C++?
JavaScript (TensorFlow.js):
async function applyNMS(boxes, scores, iouThreshold) {
const nmsIndices = await tf.image.nonMaxSuppressionAsync(
boxes,
scores,
maxOutputSize,
iouThreshold
);
return nmsIndices;
}
C++ (OpenCV):
#include <opencv2/dnn.hpp>
std::vector<int> indices;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(
boxes, // std::vector<Rect>
confidences, // std::vector<float>
conf_threshold,
iou_threshold,
indices
);
Q7: Tại sao có khi detections bị “nhấp nháy” (flickering) trong video?
Nguyên nhân:
- Confidence score dao động quanh threshold
- Boxes không ổn định giữa các frames
Giải pháp:
# 1. Temporal smoothing
def smooth_detections(current_dets, prev_dets, alpha=0.7):
"""Smooth boxes giữa các frames"""
smoothed = alpha * current_dets + (1 - alpha) * prev_dets
return smoothed
# 2. Tracking
# Sử dụng tracking algorithms (DeepSORT, ByteTrack)
tracker = DeepSORT()
tracked_objects = tracker.update(detections)
Q8: Performance của NMS trong real-time apps?
Benchmarks (YOLOv8n, 640x640, CPU):
| Stage | Time | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Preprocessing | 2ms | 10% |
| Inference | 15ms | 70% |
| NMS | 4ms | 20% |
| Total | 21ms | 100% |
Kết luận: NMS chỉ chiếm ~20% thời gian, không phải bottleneck!
7. Kết Luận
🎯 Key Takeaways
- NMS là bắt buộc khi deploy YOLO models sang các format khác
- Class-Aware NMS tốt hơn Class-Agnostic cho general object detection
- Tuning thresholds (
conf_threshold,iou_threshold) rất quan trọng - Vectorized operations giúp tăng tốc đáng kể
- Testing trên nhiều scenarios để tìm best settings
📚 Kiến Thức Bạn Đã Học
- ✅ Hiểu output thô của YOLO models (8400 × 84)
- ✅ Cách tính IoU giữa 2 bounding boxes
- ✅ Quy trình 5 bước của NMS post-processing
- ✅ Implement NMS từ đầu bằng NumPy
- ✅ Best practices và common pitfalls
- ✅ Tips để optimize performance
🚀 Next Steps
- Practice: Implement NMS cho custom datasets
- Experiment: Test với các IoU thresholds khác nhau
- Deploy: Port code sang JavaScript/C++ cho production
- Advanced: Tìm hiểu Soft-NMS, DIoU-NMS
- Tracking: Combine NMS với object tracking algorithms
📖 Tài Liệu Tham Khảo
- Ultralytics YOLOv8 Official
- YOLO Post-Processing Guide
- Original NMS Paper
- Soft-NMS Paper
- ONNX Runtime Documentation
🙋♂️ Có Thắc Mắc?
Nếu bạn có câu hỏi hoặc gặp vấn đề khi implement NMS, feel free để lại comment bên dưới! Mình sẽ cố gắng trả lời sớm nhất có thể.
Happy Coding! 🚀
Bài viết được viết bởi Le Hoang Viet
Cập nhật lần cuối: 17th Feb 2026
